Dec 16, 2020 | Civil Rights Law, Constitutional Rights, Police Misconduct
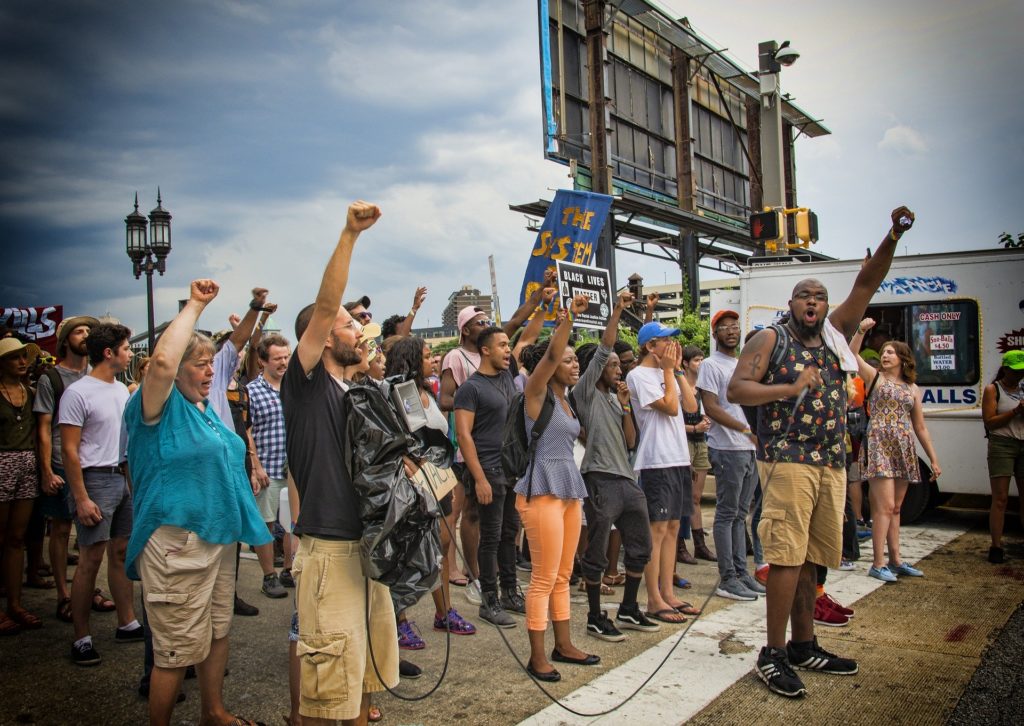 Over the summer, Denver saw weeks of protests in reaction to the death of George Floyd. And, unfortunately, some police brutality. The majority of the protests in Denver centered around the Capitol and while most people came to protest peacefully, violence erupted, and many people were injured or exposed to chemical weapons. It now appears that protesters might not be as blameworthy as had been previously reported. A recent investigation has found that police may have needlessly caused some of the violence.
Over the summer, Denver saw weeks of protests in reaction to the death of George Floyd. And, unfortunately, some police brutality. The majority of the protests in Denver centered around the Capitol and while most people came to protest peacefully, violence erupted, and many people were injured or exposed to chemical weapons. It now appears that protesters might not be as blameworthy as had been previously reported. A recent investigation has found that police may have needlessly caused some of the violence.
Police brutality and the Denver Police Department (DPD)
A recent article from Denverite (Police officers acted dangerously and anonymously during protests against police brutality and racism, investigation finds) discusses a recent investigation regarding the DPD’s response to the protests. The investigation found that the police used “unwarranted and reckless violence” and that “a lack of body camera footage and missing or vague documentation amounted to a mismanaged response from the very institution being protested.” There have been instances where the police violated their own polices by not giving orders to the crowds to disperse before using pepper spray, pepper balls, and other weapons — often recklessly. It also found that officers continued to use chemical weapons and explosives after people had started to disperse, and that some of the officers hadn’t been trained to use those weapons.
The investigation and report are from The Office of the Independent Monitor, which is “charged with working to ensure accountability, effectiveness, and transparency in the Denver Police and Sheriff disciplinary processes.” The biggest problem they found regarding the actions taken during the protests was the lack of transparency. Body camera were frequently left off. Video footage was frequently not uploaded, and officers didn’t file use-of-force reports. Many officers failed to identify themselves and/or display their badge numbers. DPD even failed to document which officers was deployed during the first four days of the protest. That makes it difficult to assess blame in the more than 100 complaints received of officer misconduct. But mostly, the report found that the Denver Police Department needs to reform its use of force, body camera practices, and officer use of specific weapons.
Were you a victim of police brutality at the protests?
If you were injured by the unnecessary force of police officers during the protests this summer, we would like to hear your story. Police brutality is illegal and officers do not have the right to violate your constitutional rights. If the police have violated your rights and caused injuries, you may be able to file a claim to recover damages fight to ensure justice is served A civil rights attorney can help you determine whether a civil rights action should be filed.
If you or a loved one are the victims of police brutality or other law enforcement abuses, call the Civil Rights Litigation Group at (720) 515-6165 or use our online contact form. Schedule your free consultation with a Denver civil rights attorney today.
720-515-6165
Additional articles and resources:
Denver police use chemicals to deter people protesting police violence as downtown erupts in chaos
Office of the Independent Monitor
Attorneys hint at massive lawsuit against Denver for police department’s response to summer protests
Additional posts on this topic:
What are my rights if I protest the police?
Police brutality cases in Colorado and your rights
How do I report police brutality in Denver?
Nov 28, 2020 | Civil Rights Law, Constitutional Rights, Police Misconduct
 When people think about police misconduct, the first thing that comes to mind is usually police brutality — and that’s understandable considering the vast amount of press coverage from cases like George Floyd this year. But there are many other ways that the police can and have engaged in illegal conduct and have violated people’s civil rights. It is important to understand what they can and can’t do so that you can protect yourself.
When people think about police misconduct, the first thing that comes to mind is usually police brutality — and that’s understandable considering the vast amount of press coverage from cases like George Floyd this year. But there are many other ways that the police can and have engaged in illegal conduct and have violated people’s civil rights. It is important to understand what they can and can’t do so that you can protect yourself.
Witness tampering and police misconduct
There have been many examples of the police getting caught in bad situations and then attempting to coerce witnesses to change how the evidence looks – for the police and the people police arrest. In Maui in 2015, Anthony Maldonado was accused of stealing $1800 from a person he had stopped. That right there is a crime, but after the victim reported it, Maldonado and several other officers tried to bribe the person to withdraw the complaint. Maldonado eventually pled guilty to witness tampering.
It is absolutely illegal for an officer to attempt use their power or authority as a police officer to attempt to get a witness to change their true testimony to something false or to unduly influence a complaining party to withdraw a complaint. But it happens all the time as officers have power and many people fall victim to their threats.
This type of misconduct can lead to criminal sanctions and even civil rights lawsuits for damages, if the conduct violates a persons’ constitutional rights.
Planting or fabricating evidence
If a case isn’t looking the way an officer thinks it should, they may decide to plant, fabricate, remove, or lie about evidence. One such example involves Richard Pinheiro, an officer in the Baltimore Police Department. His body camera actually caught him tampering with evidence at a crime scene. Unfortunately, fabricating evidence is a misdemeanor in Maryland so even though he was convicted, he is still on the job. Incidents like this also highlight the issue of bad cops being allowed to remain on the job.
Another example involved Michael Slager, an officer in North Charleston who shot and killed Walter Scott and then planted a taser near his body to back up his story that Scott was armed. Slager eventually received a 20-year sentence after a man came forward with a cellphone recording of the incident. Had a passerby not filmed the encounter, Slager likely would have gotten away with his crimes. This is one more example of why you should always record any police encounters you may witness.
This type of misconduct can lead to criminal sanctions if it is revealed, and possibly civil rights lawsuits for damages if the conduct violates a persons’ constitutional rights – such as when the lies/fabrications cause a person to be improperly jailed and/or prosecuted for a crime they didn’t commit.
When does police misconduct violate my civil rights?
While the behaviors mentioned above are definitely illegal, they do not always involve civil rights violations. For example, the most common civil rights violation applicable to manipulating or fabricating evidence is wrongful prosecution. However, in order to make that type of civil rights claim, there are several things you must be able to prove. For example, you must be able to show that the officer caused or continued a criminal prosecution where there was no probable cause to believe that a crime had been committed in the first place. You must also show that the officer created, planted, or lied about evidence that the prosecution relied on to prosecute the case. The criminal case against you must legitimately be terminated in your favor. You also have to be able to prove that the officer did all of this with malice and that it caused some sort of injury.
Reporting this type of misconduct so that appropriate criminal sanctions can be taken against officers is often the first step to getting bad officers removed from the police force. Filing civil rights lawsuits in appropriate circumstances is key to obtaining compensation when your rights have been violated. If you are faced with such circumstances, you want a lawyer that is 100% dedicated to understanding and helping you navigate these types of complexities.
We are here to help with protecting your civil rights
If you have experienced problems with your civil rights being violated by the police, please give us a call. We work diligently to protect civil rights. For a free, no-obligation consultation with the Civil Rights Litigation Group, contact our Denver CO law firm today at (720) 515-6165 or use our online contact form.
Oct 20, 2020 | Civil Rights Law, Constitutional Rights, Discrimination, Uncategorized
 When Associate Justice Ruth Bader Ginsberg passed away last month, she left an impressive legal legacy in her fight for civil rights. Throughout her career — both as an attorney and a judge — she fought everyone to have equal protection under the law.
When Associate Justice Ruth Bader Ginsberg passed away last month, she left an impressive legal legacy in her fight for civil rights. Throughout her career — both as an attorney and a judge — she fought everyone to have equal protection under the law.
Civil rights and the Supreme court
Before becoming a member of the Supreme Court, she won five cases before them based on the equal protection clause of the 14th Amendment — specifically the section that guarantees all citizens of the U.S “equal protection of the laws.” Early in her career, Ginsberg worked with the ACLU and led their campaign for gender equality, arguing more than 300 gender discrimination cases. Before her, the amendment was primarily used to argue for racial equality, but she successfully used it to fight for gender equality. She carefully chose cases that would highlight the inequality in how men and women were treated. She found success by taking on cases where men were the ones suffering discrimination.
In 1971, she argued in Reed v. Reed that an Idaho law stating that “males must be preferred to females” when determining the administrator of an estate was a direct violation of the 14th Amendment. The reasoning was that men were better at math. The Supreme Court unanimously agreed that the law was wrong.
In 1973, she won Frontiero v. Richardson, where her client was the husband of a female Air Force officer who was denied spousal death benefits because women were not considered the primary economic providers for their families.
Again, in 1975, in Weinberger v. Weisenfeld, she sued for a male client who had been denied Social Security survivor benefits because the agency assumed that men wouldn’t need them because they earned more money that their wives ever did. By arguing that gender discrimination hurts men as well as women, she was able to use the 14th Amendment to gain more equal rights for women. Her wins also discouraged state legislatures from writing any new laws that drew distinctions based on gender.
Using the 14th Amendment for other types of civil rights cases
After Ginsberg used the 14th Amendment to argue non-race-based discrimination cases, it opened the doors for other lawyers to use it civil rights cases for the LGBTQ community. In 1996, it was used in Romer v. Evans to overturn Colorado’s infamous Amendment 2 that prohibited LGBTQ citizens from claiming discrimination.
In 2015, it was used in the landmark Obergefell v. Hodges case that required all states to recognize same-sex marriages that were performed in other states.
Fighting for civil rights on the Supreme Court
Once she was appointed to the Supreme Court, Ginsberg continued her fight for gender equality and civil rights. In United States v. Virginia, she wrote the majority opinion that struck down the admissions policy at the Virginia Military Institute. Once again using the 14th Amendment, she argued that a state-run institution could not use gender as a basis for denying women the opportunity to attend the school.
In addition to gender equality cases, she also wrote opinions about prisoner rights. In Cutter v. Wilkinson, she argued in favor of prisoners’ religious rights. And before she was on the Supreme Court, she would have all her law clerks visit prisons so they better understood what was at stake in the cases they assisted her with.
While not all of her opinions, cases and writings are considered perfectly in line with promoting civil rights, the sum of her life’s work absolutely shows the impact she had in arguing that the law should treat everyone equally. Her actions both as an attorney and a judge will be felt for generations to come.
Additional posts about civil rights and discrimination
Sexist language and subtle discrimination
Dealing with disability discrimination in the workplace
Is there such a thing as pregnancy discrimination in the workplace?
Discrimination in Denver
Your Denver civil rights attorney
If you believe your civil rights have been violated, whether through police misconduct or discrimination, our civil rights attorneys can help you. Call the Civil Rights Litigation Group at 720-515-6165 or use our online contact form. Schedule your free consultation with a Denver discrimination attorney today.
Call us at 720-515-6165
Aug 31, 2020 | Civil Rights Law, Constitutional Rights, Discrimination, Employee Rights
 Most people can recognize sexist language as it’s often quite obvious, such as a man referring to a female employee’s looks, saying suggestive things about her, or calling her pet names like “honey” or baby.” But more often than not, it’s the subtle ways people use sexist language that can reveal gender bias or discrimination tendencies.
Most people can recognize sexist language as it’s often quite obvious, such as a man referring to a female employee’s looks, saying suggestive things about her, or calling her pet names like “honey” or baby.” But more often than not, it’s the subtle ways people use sexist language that can reveal gender bias or discrimination tendencies.
And while we are specifically referring to women in this post, know that sexist language can apply to both men and transgendered individuals as well.
Sexist language in the White House
Many people would agree that Donald Trump is pretty misogynistic because he has said some very derogatory things about women, especially when it comes to their looks. But it’s the more subtle wording he uses that implies an even deeper bias. He’s never been one to shy away from verbally attacking anyone he perceives as a threat — whether a man or woman — but the ways he chooses to insult people can be revealing.
For instance, while he is famous for using the phrase “nasty woman,” there are many instances where he has also called men nasty. However, he tends to reserve use of the word “mean” almost exclusively when discussing women. The term often implies how one person treats another person, or that they are ” offensive, selfish, or unaccommodating.” (https://www.dictionary.com/browse/mean?s=t). That definition suggests that the women Trump calls mean make him feel offended or like he isn’t worthy — a feeling that could denote unmanliness if Trump were to use it to describe a man.
Here are two examples of Trump referring to Elizabeth Warren as mean:
“…You got so horrible to people and they said you know she’s, not dumb, but she’s just so damn mean, we can’t vote for her. She’s a mean one. She is mean.” (https://factba.se/transcript/donald-trump-speech-kag-rally-north-charleston-south-carolina-february-28-2020)
“… But people don’t like her. She’s a very mean person, and people don’t like her. People don’t want that. They like a person like me, that’s not mean….”
(https://factba.se/transcript/donald-trump-remarks-coronavirus-emergency-funding-march-6-2020)
By comparison, when Trump refers to a man as mean, it’s in a complimentary way:
“… We have a man who’s smart as hell, and he is tough, and he is mean and nasty, but he loves this state, and he’s only mean and nasty because he wants to defend you and me, and all of the horrible things that we all go through…”
(https://factba.se/transcript/donald-trump-speech-kag-rally-dallas-texas-october-17-2019)
Sexist language in the workplace
While the obvious sexist language and behaviors are frowned upon and generally avoided in the workplace, it’s the more subtle sexism that seems to be taking over. The problem is that many people still place men and women in certain gender roles and have specific expectations for them. “Communal language is mainly applied to women, and it invokes stereotypical female traits like being supportive, showing warmth, and helping the team. Agentic [authoritative] language is mainly applied to men and is more about getting the job done, taking charge, and being independent.” (https://www.bbc.com/worklife/article/20170329-the-hidden-sexism-in-workplace-language) So, while a man who is good at his job might be referred to as confident or a leader, a woman acting the same might be called bossy or abrasive — the implication being that it’s okay for men to act in an authoritative way but not women.
” A 2014 study for Fortune.com by Kieran Snyder examined 248 reviews from 180 people, (105 men and 75 women). The reviews came from 28 different companies, all in the tech sector, and included a range of organisational sizes. One word appeared 17 times in reviews of women, and never in any of the reviews of men: ‘abrasive’. Other words were disproportionately applied to women, including bossy, aggressive, strident, emotional and irrational. Aggressive did appear in two reviews of men, in the context of them being urged to be more aggressive. Reviews of women only ever used aggressive as a criticism. The gender of the person writing the review didn’t affect the results of the study.” (http://sacraparental.com/2016/05/14/everyday-misogyny-122-subtly-sexist-words-women/)
Sexist language hidden in compliments
Another subtle way that sexist language can appear is in compliments, but ones that are reserved specifically for one gender. For example, the words “modest,” “vivacious,” and “ladylike” are words that are almost exclusively used to describe women. If she’s modest and ladylike, then she doesn’t exert her sexuality. If she’s vivacious or bubbly, then she’s pleasant to be around and isn’t too abrasive. And while they may sound nice, they all imply that the woman isn’t a threat to the men around her and that she’s valued for how she treats people and acts, as opposed to how good of an employee she is. And while some people may see these subtle compliments as harmless, they can affect not only how women think about themselves in the workplace but how they are perceived by their superiors, which may limit their advancement potential.
Determining discrimination and sexism in the workplace
Here are some questions to consider whether you are being discriminated against:
- Are there consistent incidents of sexist language being used against you and other women?
- Is there a pattern of bias or discrimination against women consistently being passed over for promotions or job transfers?
- Are complaints of sexism being ignored?
- Have you or others recently reported wrongdoing, but are now being retaliated against? (Fewer work hours, demotion, pay cut, etc.)
- Have you consistently done a good job, but are now receiving disciplinary notices?
These are just some of the ways you may be able to determine if there is discrimination and not a complete list of questions to ask.
____________________________
Your Denver Discrimination attorney
If you feel that you have been discriminated against in the workplace and believe that sexist language may have played a part, our civil rights attorneys can help you. If you or a loved one has suffered sexist discrimination violation in your place of employment, call the Civil Rights Litigation Group at 720-515-6165 or use our online contact form. Schedule your free consultation with a Denver discrimination attorney today.
Call us at 720-515-6165
Jul 21, 2020 | Civil Rights Law, Constitutional Rights, Employee Rights
 Amidst all the civil rights protests lately, one divisive topic has emerged: Is it a violation of my civil rights for the government to require me to wear a face mask in public? In short, probably not. Because of the rapid increase in Covid-19 infections, many states have issued temporary laws, requiring all citizens (over the age of 11, in Colorado) to wear face masks. In Colorado, it applies while “entering or moving within any public indoor space [or] while using or waiting to use public (buses, light-rail) or non-personal (taxis, car services, ride-shares) transportation services.” You aren’t required to wear them in private residences or when outdoors, unless you are waiting for public transportation. Given the public-available data on the Covid pandemic, face-mask orders probably bear a reasonable relationship to the emergency and are probably legal, based on pre-existing case law.
Amidst all the civil rights protests lately, one divisive topic has emerged: Is it a violation of my civil rights for the government to require me to wear a face mask in public? In short, probably not. Because of the rapid increase in Covid-19 infections, many states have issued temporary laws, requiring all citizens (over the age of 11, in Colorado) to wear face masks. In Colorado, it applies while “entering or moving within any public indoor space [or] while using or waiting to use public (buses, light-rail) or non-personal (taxis, car services, ride-shares) transportation services.” You aren’t required to wear them in private residences or when outdoors, unless you are waiting for public transportation. Given the public-available data on the Covid pandemic, face-mask orders probably bear a reasonable relationship to the emergency and are probably legal, based on pre-existing case law.
Does the government have the legal authority to mandate face masks?
Probably. Since we are in the middle of a public health emergency, state and local officials have the authority to issue and enforce reasonable rules of safety. According to Colorado Attorney General Phil Weiser, “This has been upheld repeatedly. No one has the right to expose the community to communicable disease.” Likewise, Colorado Governor Jared Polis has emergency powers that grant him the right to issue the face mask mandate, and that authority is upheld by the Colorado state constitution (Article IV, Section 2). A law passed by the legislature: Colorado Disaster Emergency Act, CRS 24-33.5-701 also supports this.
A state government’s power to issue orders that are reasonably related to the protection of other citizens during public health emergencies has also been upheld by the Supreme Court. This has been the case since 1905, when the Supreme Court ruled on Jacobson v. Massachusetts. The case involved a smallpox outbreak and local authorities mandated that everyone had to be vaccinated against it or risk a fine (unless medically unable to do so safely). The court upheld this authority, saying, “Upon the principle of self-defense, of paramount necessity, a community has the right to protect itself against an epidemic of disease which threatens the safety of its members.”
“The public health expert consensus is that wearing a mask in public is a key countermeasure in combating the coronavirus pandemic because it helps slow the infection rate. Even cloth face masks can help curb community spread of coronavirus, in part by reducing transmission by people who are infected but experience no symptoms. The coronavirus pandemic is the kind of extraordinary circumstance when the public good outweighs individual inconvenience.” (Law.com)
To date, over 500,000 Americans have died from Covid-19, so it is likely within each state government’s authority to mandate necessary requirements issued for the purpose of protecting the health and safety of those who have not yet been infected, so long as those requirements relate directly to the cause at hand. Since Covid-19 has been shown to be spread by people breathing out tiny droplets that may contain the virus, face masks are likely to be considered a reasonable precaution. Face mask requirements are even more likely to be considered reasonable considering that many people who have the virus are asymptomatic and may unknowingly spread it to others. To date, the Supreme Court has had the opportunity to revisit this issue, several times, but has declined in all but religious liberty cases, where certain government’s have been deemed to have applied face mask mandates inequitably to religious institutions and/or religious activates, as compared to similarly situated secular institutions/activities.
Can I be required to wear face mask if I have a medical condition?
For those people “who cannot medically tolerate a face covering,” the ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) requires that businesses, government entities, etc. make reasonable accommodations. Those may include offering delivery or curb-side pickup of things like groceries and goods, or offering online options for accessing services such as renewing a license. However, they aren’t required to allow you in their space without a mask, as that could endanger others.
The definition for those medically exempt from the order is pretty narrow: “a person who has trouble breathing or anyone who is unconscious, incapacitated, or otherwise unable to remove the cloth face-covering without assistance.” It doesn’t include people who believe the mask will cause them to breathe in carbon dioxide or lower their oxygen levels.
The ADA has also issued a warning against using fake mask exemption cards that have flooded the internet. “The ADA does not provide a blanket exemption to people with disabilities from complying with legitimate safety requirements necessary for safe operations.” (ADA website)

Can a business refuse me entry if I won’t wear a mask?
Not only can a business refuse you entry, but they may be required to as they are responsible for upholding the state and local laws for face masks and other safety measures. Again, they have to make reasonable accommodations for those with disabilities, so if you suffer from a disability, you should be prepared to make a specific request for accommodation that will not create an undue burden on the business. But as long as the business is enforcing the mask requirement equally to everyone, they are probably not violating your rights. Businesses are also required to post signage stating that masks are required. If you attempt to enter a business without a mask, you could be subject to allegations of trespassing. Likewise, businesses that do not enforce the ordinance may lose their license.
Can my employer require me to wear face masks?
Because of the mandate, employers must require all employees to wear masks. They have to make reasonable accommodations for employees with disabilities and should offer protection to those at a greater risk of severe illness due to Covid-19. Some employers may require employees to wear additional protective gear, such as gloves, and some are required to per Public Health Order 20-31.
If you are in a job that requires specific high-end protective gear like N95 masks, employers in Colorado are required to provide them. For all other businesses, government entities, etc. the Safer at Home public health order from March states that employers shall “provide appropriate protective gear like gloves, masks, and face coverings.” The newest public health order states that employers “should” provide protective equipment, but doesn’t specifically mandate it.
Regardless, employers are still required to provide workplaces “free from recognized hazards likely to cause death or serious physical harm” under the Occupational Safety and Health Act’s General Duty Clause. This is interpreted differently for each business and can include things like putting up clear barriers to protect employees who come in close contact with the public.
Other resources on our blog:
Additional resources:
Face-Covering Requirements and the Constitution
Colorado Mask Order: When Do I Need To Wear A Face Covering? (And More Mask Questions Answered)
Questions & answers about the statewide mandatory mask order
Considerations for Wearing Cloth Face Coverings
Jun 26, 2020 | Constitutional Rights, Police Misconduct

Colorado has one of the worst rates of police shootings in the country. And the record on police accountability is just as bad:
“In all but two of the 309 cases in six years, officers’ actions were legally justified by district attorneys or grand juries.”
It will increase police transparency and accountability by requiring body cameras
On or before July 1, 2023, the bill requires all law enforcement agencies in the state of Colorado to wear and use body-worn cameras during interactions with everyday people.
“A peace officer shall wear and activate a body-worn camera when responding to a call for service or during any interaction with the public initiated by the peace officer, when enforcing the law or investigating possible violations of the law.“
Not only will all officers be required to wear body cameras, but those that do can face penalties for turning off or tampering with the cameras. Also, departments will be required to release footage within 21 days after a misconduct allegation. We highly recommend that you make complaints of misconduct with the Internal Affairs Division of any police agency who you believe may have committed misconduct.
The bill limits use of chokeholds
Any type of chokehold or carotid hold will be banned unless absolutely necessary, and only when dealing with violent offenses. Officers will not be allowed to use deadly force against anyone suspected of a minor or nonviolent offense.

Police will be required to intervene to prevent excessive force or face new penalties for the ‘failure to intervene’
One of the biggest problems with the current system of police accountability is that supposed good cops often stand by while bad cops assault or even kill people, as was the case with George Floyd in Minneapolis. Under the new law, officers who fail to stop other officers from using unnecessary excessive force could face new charges. There are also provisions to protect those officers from retaliation when they do intervene.
New database will keep a record of police misconduct and problem police officers to improve police accountability
In the past, many officers were able to remain on the force because misconduct violations were often erased from their records after a short amount of time, eliminating any possibility for police accountability. Even for serious offenses, they could simply move to a different state and get hired by a new department. Starting on January 1, 2022, this new database will require a database entry be made for any officer who has been fired, decertified, found to have lied, or failed to follow training requirements. Also, any officer who is convicted of (or pleads guilty to) using excessive force, failure to intervene to stop excessive force, would permanently lose their Peace Officer Standards and Training board certification, which is required to serve as a peace officer in Colorado.
While the bill still leaves open a gaping loophole for officers who choose to quit amid investigation of police misconduct against them, it does require a new level of documentation so that problem officers can be identified and police accountability can be improved.
The Qualified Immunity Defense will be removed for violations of the Colorado State Constitution and officers will be made to pay
Until now, one of the biggest issues with police accountability is that officers were shielded from liability for novel ways in which they could think up or act to violate the constitutional rights of victims. Qualified immunity, under federal law, completely shields officers from liability when the same, precise, conduct has not been held to be a violation of someone’s rights in prior appellate decisions. Even worse, appellate courts could avoid making any determinations of whether an officer’s conduct violated the constitution merely by pointing to a lack of prior cases that fail to examine that exact conduct, because it had not been “clearly established,” beyond debate,” to “every police officer” before. As you might imagine, this led to a catch-22 in which officers have been let off the hook in litigation for excessive force in a whopping 57% of cases.
The new bill will allow people to file civil rights violations against officers individually for violations of the Colorado Constitution and qualified immunity may not be invoked as a defense in such state actions. Many of the same rights afforded by the federal Constitution are also enshrined in our state Constitution. Moreover, under this new law, individual officers will be forced to pay a small portion of judgments against them, instead of leaving it completely up to the city or county that employs them.
“If the peace officer’s employer determines the officer did not act upon a good faith and reasonable belief that the action was lawful, then the peace officer is personally liable for 5 percent of the judgment or $25,000, whichever is less, unless the judgment is uncollectible from the officer, then the officer’s employer satisfies the whole judgment.” (Enhance Law Enforcement Integrity bill, Colorado General Assembly)

Police accountability at protests
In direct response to the recent protests in Denver, the new bill prohibits officers from using any kind of chemical irritant like tear gas or pepper spray without first sufficiently announcing it and then giving people enough time to leave and get to safety. It also prohibits them from indiscriminately firing rubber bullets into crowds, as well as specifically at people’s heads, torsos, and backs. Rubber bullets have been shown to cause serious injuries.
We are here to help if you are the victim of police misconduct or violence
If you have been the victim of police misconduct, please give us a call. We work diligently to ensure police accountability and fight those who violate your civil rights. For a free, no-obligation consultation with the Civil Rights Litigation Group, contact our Denver CO law firm today at (720) 515-6165 or use our online contact form.
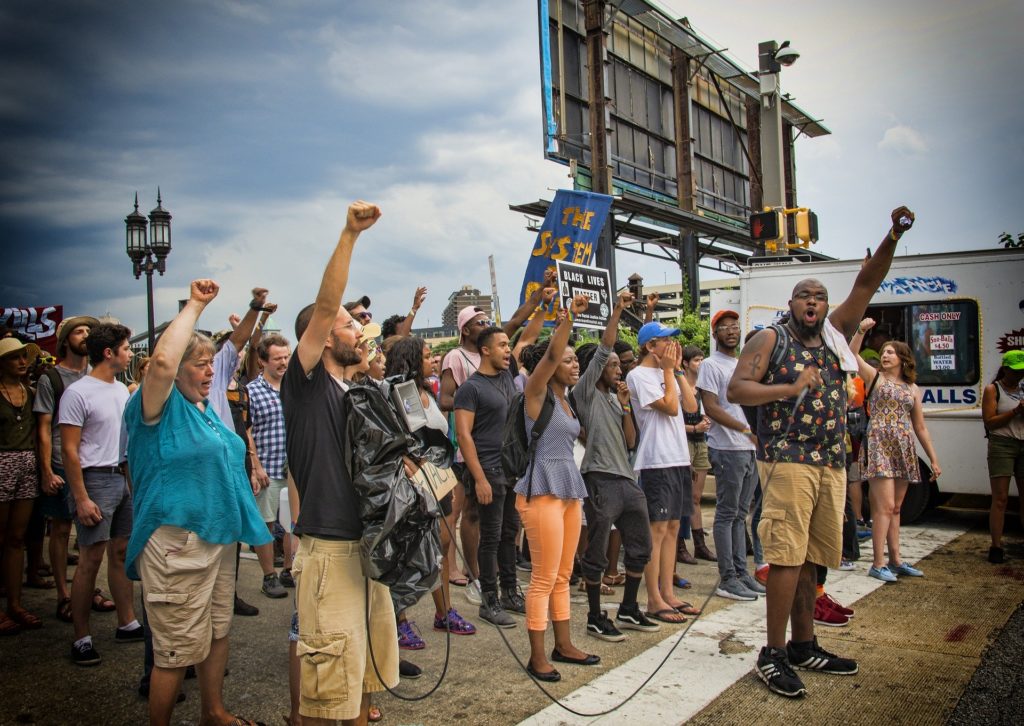 Over the summer, Denver saw weeks of protests in reaction to the death of George Floyd. And, unfortunately, some police brutality. The majority of the protests in Denver centered around the Capitol and while most people came to protest peacefully, violence erupted, and many people were injured or exposed to chemical weapons. It now appears that protesters might not be as blameworthy as had been previously reported. A recent investigation has found that police may have needlessly caused some of the violence.
Over the summer, Denver saw weeks of protests in reaction to the death of George Floyd. And, unfortunately, some police brutality. The majority of the protests in Denver centered around the Capitol and while most people came to protest peacefully, violence erupted, and many people were injured or exposed to chemical weapons. It now appears that protesters might not be as blameworthy as had been previously reported. A recent investigation has found that police may have needlessly caused some of the violence.
 When people think about police misconduct, the first thing that comes to mind is usually police brutality — and that’s understandable considering the vast amount of press coverage from cases like George Floyd this year. But there are many other ways that the police can and have engaged in illegal conduct and have violated people’s civil rights. It is important to understand what they can and can’t do so that you can protect yourself.
When people think about police misconduct, the first thing that comes to mind is usually police brutality — and that’s understandable considering the vast amount of press coverage from cases like George Floyd this year. But there are many other ways that the police can and have engaged in illegal conduct and have violated people’s civil rights. It is important to understand what they can and can’t do so that you can protect yourself. When Associate Justice Ruth Bader Ginsberg passed away last month, she left an impressive legal legacy in her fight for civil rights. Throughout her career — both as an attorney and a judge — she fought everyone to have equal protection under the law.
When Associate Justice Ruth Bader Ginsberg passed away last month, she left an impressive legal legacy in her fight for civil rights. Throughout her career — both as an attorney and a judge — she fought everyone to have equal protection under the law. Most people can recognize sexist language as it’s often quite obvious, such as a man referring to a female employee’s looks, saying suggestive things about her, or calling her pet names like “honey” or baby.” But more often than not, it’s the subtle ways people use sexist language that can reveal gender bias or discrimination tendencies.
Most people can recognize sexist language as it’s often quite obvious, such as a man referring to a female employee’s looks, saying suggestive things about her, or calling her pet names like “honey” or baby.” But more often than not, it’s the subtle ways people use sexist language that can reveal gender bias or discrimination tendencies. Amidst all the civil rights protests lately, one divisive topic has emerged: Is it a violation of my civil rights for the government to require me to wear a face mask in public? In short, probably not. Because of the rapid increase in Covid-19 infections, many states have issued temporary laws, requiring all citizens (over the age of 11, in Colorado) to wear face masks. In Colorado, it applies while “entering or moving within any public indoor space [or] while using or waiting to use public (buses, light-rail) or non-personal (taxis, car services, ride-shares) transportation services.” You aren’t required to wear them in private residences or when outdoors, unless you are waiting for public transportation. Given the public-available data on the Covid pandemic, face-mask orders probably bear a reasonable relationship to the emergency and are probably legal, based on pre-existing case law.
Amidst all the civil rights protests lately, one divisive topic has emerged: Is it a violation of my civil rights for the government to require me to wear a face mask in public? In short, probably not. Because of the rapid increase in Covid-19 infections, many states have issued temporary laws, requiring all citizens (over the age of 11, in Colorado) to wear face masks. In Colorado, it applies while “entering or moving within any public indoor space [or] while using or waiting to use public (buses, light-rail) or non-personal (taxis, car services, ride-shares) transportation services.” You aren’t required to wear them in private residences or when outdoors, unless you are waiting for public transportation. Given the public-available data on the Covid pandemic, face-mask orders probably bear a reasonable relationship to the emergency and are probably legal, based on pre-existing case law.


